Unit I was just a very brief intro, it only accounts for 5% of the AP exam and will not be a topic for the DBQ or Long Essay. Unit II is where 'Merica really begins to take shape. Colonial regions in North America are settled by different European nations -- France, Holland, Spain and England all vie for Colonial supremacy. Who wins? For a clue, consider what language this post is being written in. Key elements of American identity also begin to take shape -- American Exceptionalism, religious and civil liberties, education, burning witches, etc......
Unit II Key Concepts
Europeans and American Indians maneuvered and fought for dominance, control, and security in North America, and distinctive colonial and native societies emerged.
Key Concept 2.1: Europeans developed a variety of colonization and migration patterns, influenced by different imperial goals, cultures and the varied North American environments where they settled, and they competed with each other and American Indians for Resources.
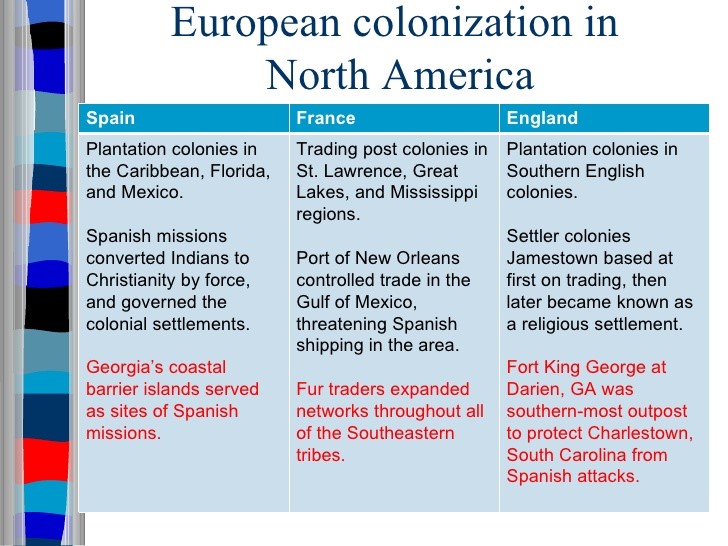
I. Spanish, French, Dutch, and British colonizers had different economic and imperial goals involving land and labor that shaped the social and political development of their colonies as well as their relationships with native populations.
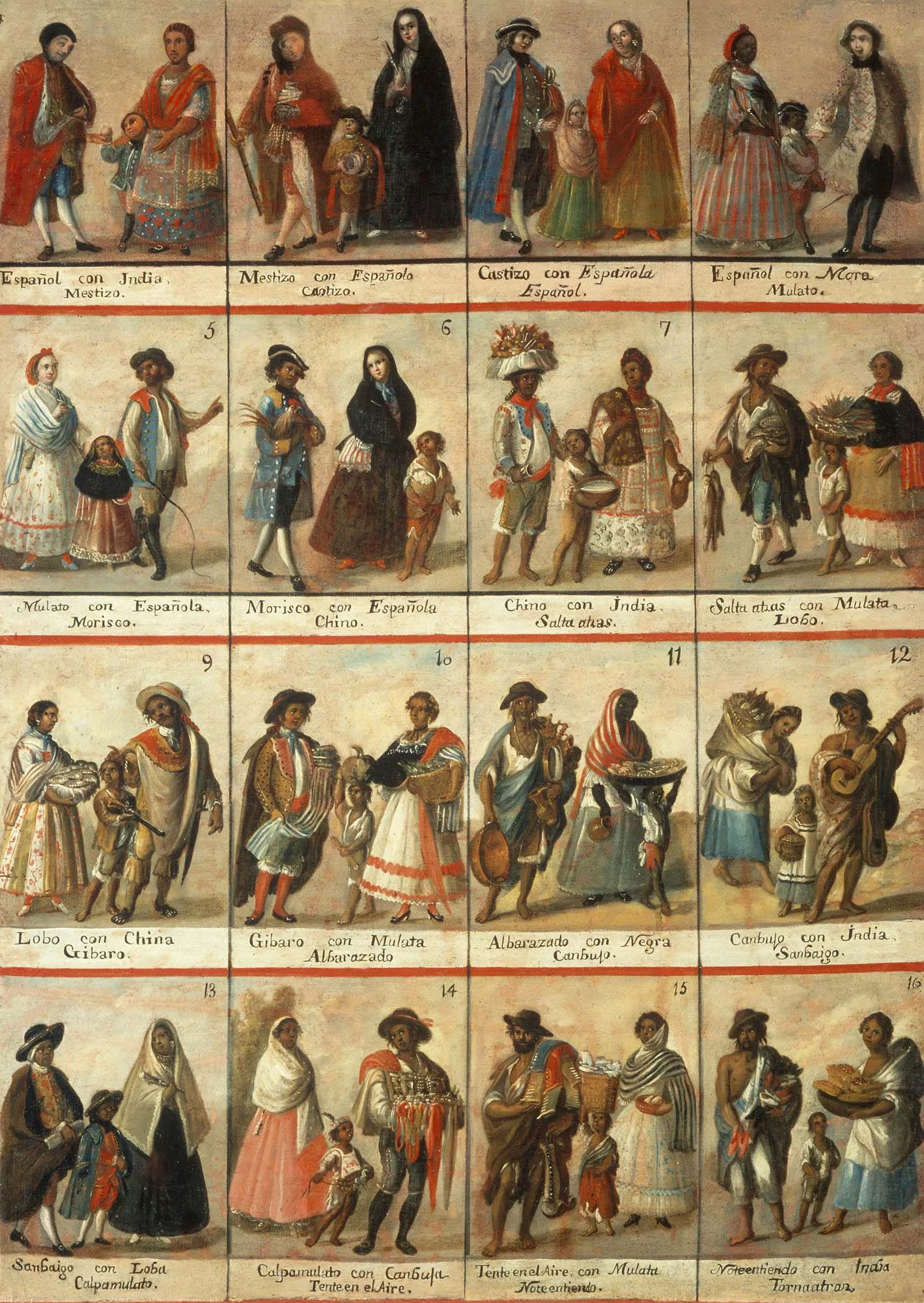
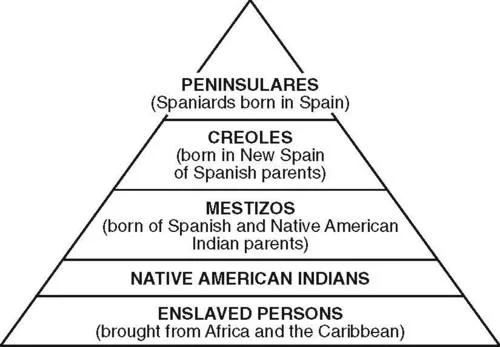
A. Spanish efforts to extract wealth from the land led them to develop institutions based on subjugating native populations, converting them to Christianity, and incorporating them, along with enslaved and free Africans, into the Spanish colonial society.
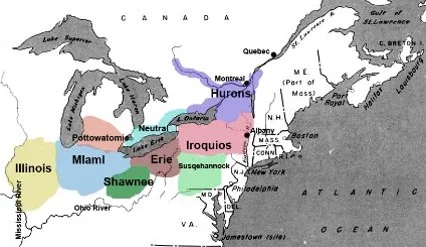
B. French and Dutch colonial efforts involved relatively few Europeans and relied on trade alliances and intermarriage with American Indians to build economic and diplomatic relationships and acquire furs and other products for export to Europe.
Beaver Fur hats – hats of the 1600 and 1700’s for both men and women were made of beaver furs (desired for warmth, style, softness and color)
C. English colonization efforts attracted a comparatively large number of male and female British migrants, as well as other European migrants, all of whom sought social mobility, economic prosperity, religious freedoms, and improved living conditions. These colonists focused on agriculture and settled on land taken from Native Americans, from whom they lived separately.
Approximate number of settlers in North American colonies (ca 1700)
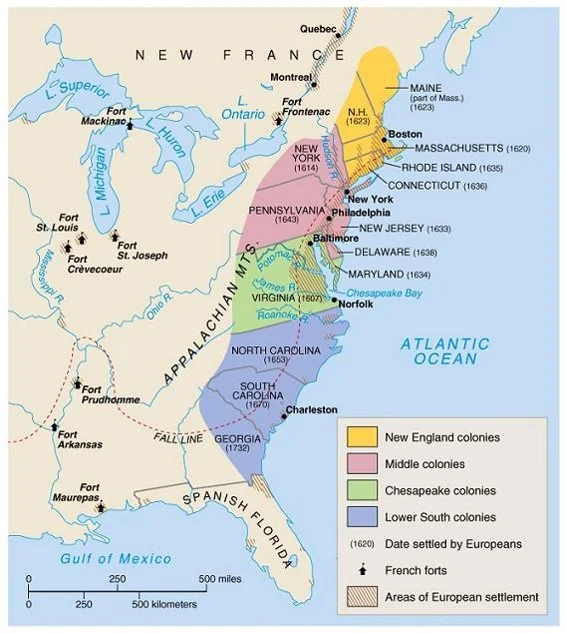
II. In the 17th century, early British colonies developed along the Atlantic Coast, with regional differences that reflected various environmental, economic, cultural and demographic factors.
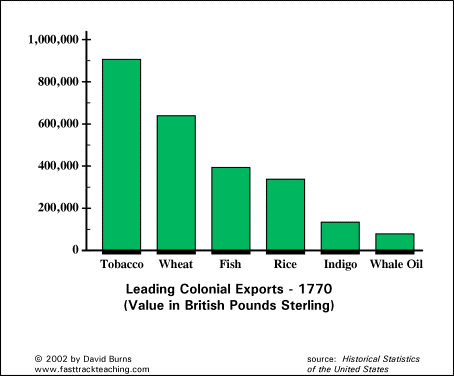
A. The Chesapeake and North Carolina colonies grew prosperous exporting tobacco -- a labor intensive product initially cultivated by white, mostly male indentured servants and Africans.
B. The New England colonies, initially settled by Puritans, developed around small towns with family farms and achieved a thriving mixed economy based on agriculture and commerce.
The Lord will be our God and delight to dwell among us, as his owne people and will commaund a blessing upon us in all our wayes, soe that wee shall see much more of his wisdome power goodnes and truthe then formerly wee have beene acquainted with, wee shall finde that the God of Israell is among us, when tenn of us shall be able to resist a thousand of our enemies, when hee shall make us a prayse and glory, that men shall say of succeeding plantacions: the lord make it like that of New England: for wee must Consider that wee shall be as a Citty upon a Hill, the eies of all people are uppon us.
-- John Winthrop, City on a Hill Sermon (1630)
C. The middle colonies supported a flourishing export economy based on cereal crops and attracted a broad range of European migrants, leading to societies with greater cultural, ethnic and religious diversity and tolerance.
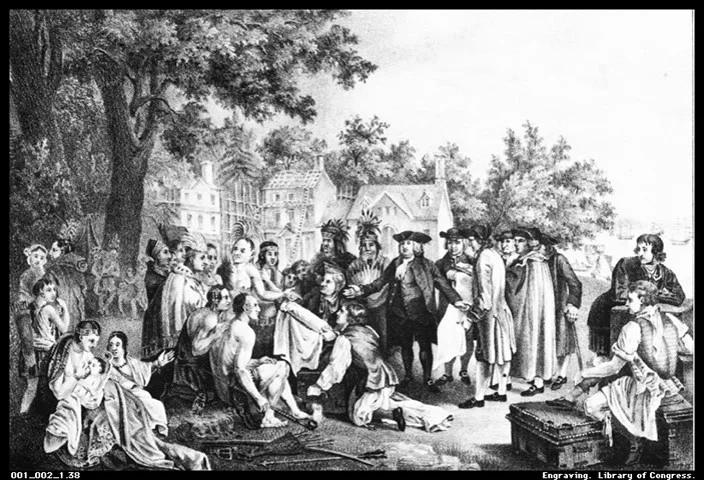
William Penn establishing the Walking Treaty with Native tribes
D. The colonies of the southern Atlantic coast and the British West Indies used long growing seasons to develop plantation based economies based on exporting staple crops. They depended on the labor of enslaved Africans, who often constituted a majority of the population in these areas and developed their own forms of cultural and religious autonomy.
S. Carolina Plantations -- Sugar and Rice/Indigo were the main crops
E. Distance and Britain's initially lax attention led to the colonies creating self-governing institutions that were unusually democratic for the era. The New England colonies based power in participatory town meetings, which in turn elected members to their colonial legislatures; in the southern colonies, elite planters exercised local political authority and also dominated the elected assemblies.
NE Town meeting
Virginia House of Burgesses (80% of delegates came from the elite planter class)
III. Competition for resources between European rivals and American Indians encouraged industry and trade and led to conflict in the Americas.
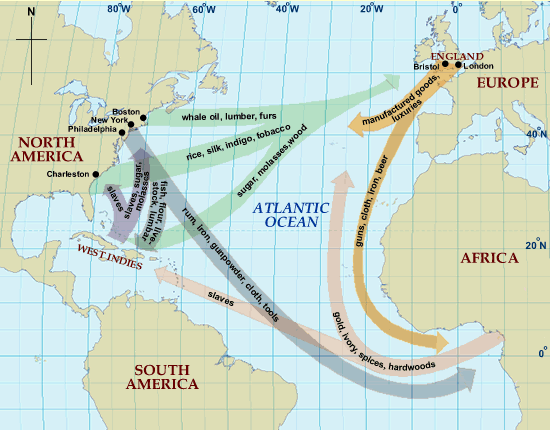
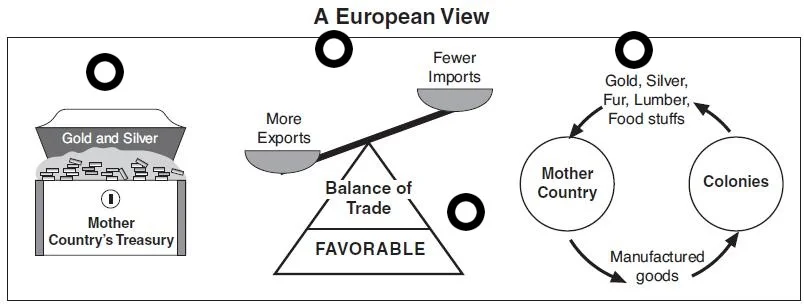
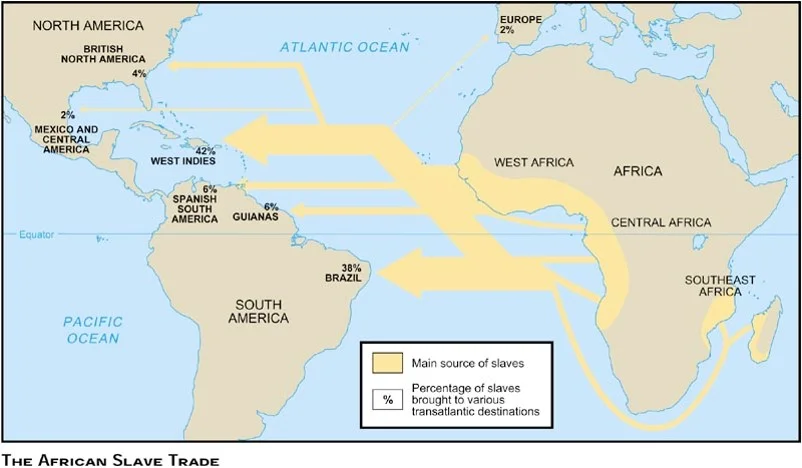
A. An Atlantic economy developed, in which goods, as well as enslaved Africans and American Indians, were exchanged between Europe, Africa and the Americas through extensive trade networks. European colonial economies focused on acquiring, producing, and exporting commodities that were valued in Europe and gaining new sources of labor.
B. Continuing trade with Europeans increased the flow of goods in and out of American Indian communities, stimulating cultural and economic changes and spreading epidemic diseases that caused radical demographic shifts.
From 1634 to 1640 the Huron Confederacy was decimated by diseases such as smallpox and measles, to which they had no immunity => this led to the dispersal of the Huron, as they no longer had the strength to fight to maintain their position in fur rich lands
C. Interactions between European rivals and American Indian populations fostered both accommodation and conflict. French, Dutch, British and Spanish colonies allied with and armed American Indian groups, who frequently sought alliances with Europeans against other American Indian groups.
E. British conflicts with American Indians over land, resources and political boundaries led to military confrontations, such as Metacom's War (King Philip's War) in New England.
F. American Indian resistance to Spanish colonizing efforts in North America, particularly after the Pueblo Revolt, saw an accommodation with some aspects of American Indian culture in the Southwest.
Key Concept 2.2: The British colonies participated in political, social, cultural and economic exchanges with Great Britain that encouraged both stronger bonds with Britain and resistance to Britain's control.
I. Transatlantic commercial, religious, philosophical, and political exchanges led residents of the British colonies to evolve in their own political and cultural attitudes as they became increasingly tied to Britain and one another.
A. The presence of different European religious and ethnic groups contributed to a significant degree of pluralism and intellectual exchange, which were later enhanced by the First Great Awakening and the spread of European Enlightenment ideas.
George Whitefield & 1st Great Awakening
Jonathan Edwards
B. The British colonies experienced gradual Anglicization over time, developing autonomous political communities based on English models with influence from intercolonial commercial ties, the emergence of a trans-Atlantic print culture, and the spread of Protestant evangelicalism.
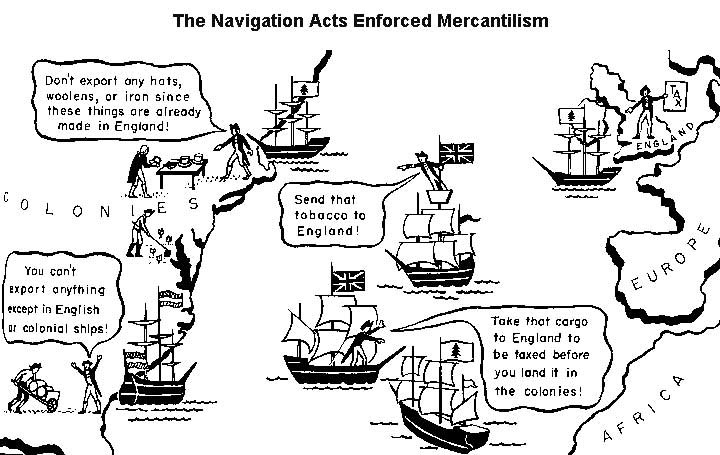
C. The British government increasingly attempted to incorporate its North American colonies into a coherent, hierarchical, and imperial structure in order to pursue mercantilist economic aims, but conflicts with colonists and American Indians led to erratic enforcement of imperial policies.
D. Colonial resistance to imperial control drew on local experiences of self government, evolving ideas of liberty, the political thought of the Enlightenment, greater religious independence and diversity and an ideology of perceived corruption in the imperial system.
II. Like other European empires in the Americas that participated in the Atlantic slave trade, the English colonies developed a system of slavery that reflected the specific economic, demographic and geographic characteristics of those colonies.
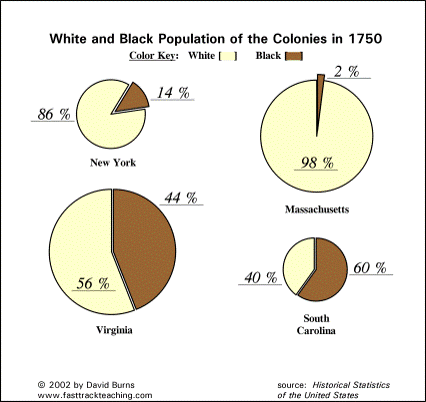
A. All the British colonies participated to varying degrees in the Atlantic slave trade due to the abundance of land and a growing European demand for colonial goods, as well as a shortage of indentured servants. Small New England farms used relatively few enslaved laborers, all port cities held significant minorities of enslaved peoples, and the emerging plantation systems in the Chesapeake and the southern Atlantic coast had large numbers of enslaved workers, while the great majority of enslaved Africans were sent to the West Indies.
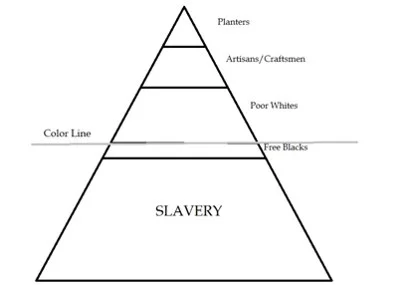
B. As chattel slavery became the dominant labor system in many southern colonies, new laws created a strict racial system that prohibited interracial relationships and defined descendants of African American mothers as black and enslaved in perpetuity.
C. Africans developed both overt and covert means to resist the dehumanizing aspects of slavery and maintain their family and gender systems, culture and religion.
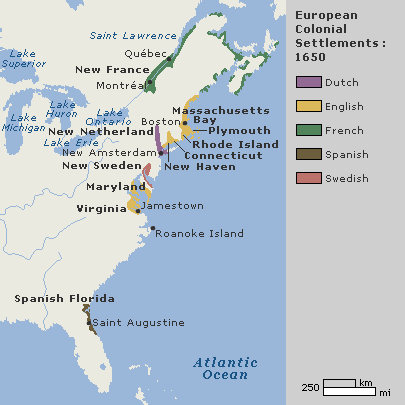
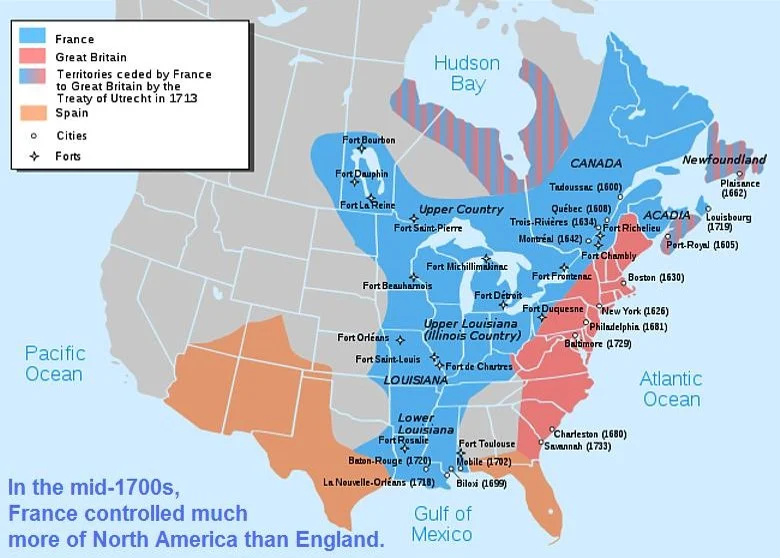
Unit II in Maps
Colonial Areas of Settlement in the 16th and 17th centuries
Colonial Settlements 1754
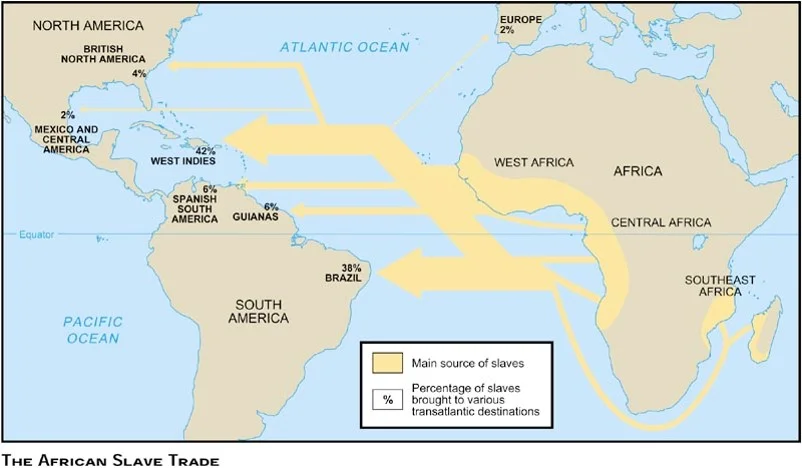
Transatlantic Slave Trade in 18th Century
English Colonial Regions in North America (18th century)
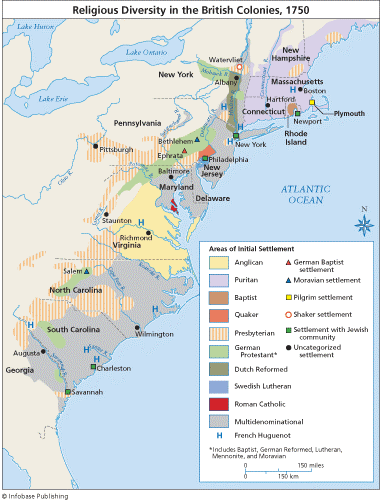
Religious Diversity in British Colonies (1750)
Est. number of Various religious adherents (1775)
- Congregationalist: 575,000(NE)
- Anglican: 500,000 (NY, South)
- Presbyterian: 410,000 (frontier)
- Lutheran: 200,000 (PA)
- Dutch Reformed: 75,000 (NY/NJ)
- Quakers: 40,000 (PA, DE)
- Catholic: 25,000 (MD)
Ethnic Percentages in Colonial North America (ca 1785)
Estimated Population elements (ca 1785)
- English and Welsh: 66%
- Scottish: 6%
- German: 4.5%
- Dutch: 2%
- Irish: 1.5%
- French: .5%
- African: 20%
Videos and Links
The Following sites and materials are useful in reviewing the content of this unit
AP Notes -- American Pageant Textbook Summaries
Click HERE to link to the textbook summary page
Gilder Lehrman AP US History
The Gilder Lehrman site offers review videos, key concepts and an interactive timeline of the era. It also contains study guides and sample essays from key topics in the time period. Visit the Gilder Lehrman AP US History Unit II website HERE