Post Civil War the nation was a disaster in many ways, but the nation was resilient and opportunity abounded. This is the age of robber barons in the cities, cowboys and Indians on the frontier and the time period when the US awoke to realize they had all the ingredients to be an industrial superpower. Raw materials (i.e. iron, coal, oil, gold, silver), abundant land (corn, wheat) and large supplies of unskilled workers (i.e. immigrants) fueled an industrial expansion that left the US as the #1 nation in steel production, oil production, and railroad track miles. What helped to fuel this expansion of course was the settlement of the US West, as many of the resources needed were supplied from this area. Of course all of this change had massive social and economic consequences for American workers and also impacted the American political system. Period VI makes up approximately 13% of the AP Exam, so pay close attention . . .
Unit VI Key Concepts
Key Concept 6.1: Technological advances, large scale production methods, and the opening of new markets encouraged the rise of industrial capitalism in the United States.
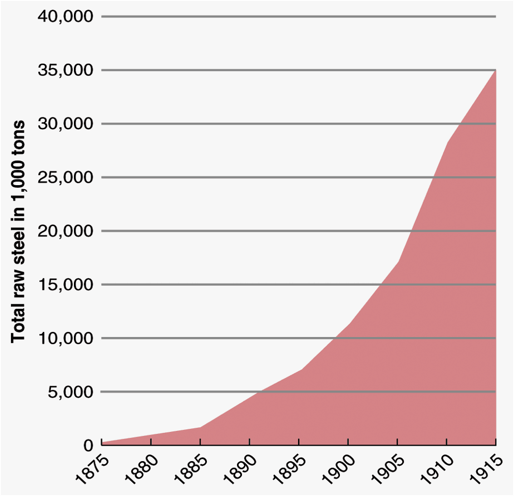
I. Large scale industrial production -- accompanied by massive technological change, expanding international communication networks, and pro growth government policies -- generated rapid economic development and business consolidation.
A. Following the Civil War, government subsidies for transportation and communication systems helped open new markets in North America.
B. Businesses made use of technological innovations, greater access to natural resources, redesigned financial and management structures, advances in marketing, and a growing labor force to dramatically increase the production of goods.
US Steel production
US patents by Decade
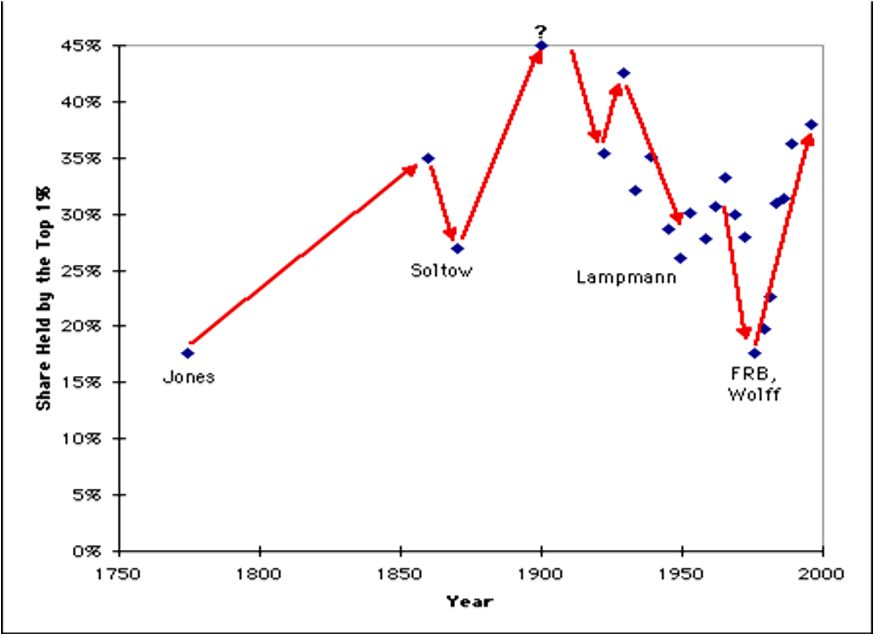
C. As the price of many goods decreased. workers real wages increased, providing new access to a variety of goods and services; many Americans standards of living improved, while the gap between rich and poor grew.
D. Many business leaders sought increased profits by consolidating corporations into large trusts and holding companies, which further consolidated wealth.
JD Rockefeller -- Standard Oil
JP Morgan -- N. Securities
Andrew Carnegie -- US Steel
E. Businesses and foreign policymakers increasingly looked outside US borders in an effort to gain greater influence and control over markets and natural resources in the Pacific Rim, Asia, and Latin America.
II. A variety of perspectives on the economy and labor developed during a time of financial panics and downturns.
A. Some argued that laissez faire policies and competition promoted economic growth in the long run, and they opposed government intervention during economic downturns.
William McKinley -- US President & big proponent of the "invisible hand"
B. The industrial workforce expanded and became more diverse through internal and international migration; child labor also increased.
C. Labor and management battled over wages and working conditions, with workers organizing local and national unions and/or directly confronting business leaders.
Samuel Gompers, President of the AFL (1884-1925)
Haymarket Affair -- Chicago 1886, Union protestors on strike threw molotov cocktails and killed 7 policeman
D. Despite the industrialization of some segments of the Southern economy -- a change promoted by Southern leaders who called for a "New South" -- agriculture based on sharecropping and tenant farming continued to be the primary economic activity in the South.
III. New systems of production and transportation enabled consolidation within agriculture, which, along with periods of instability, spurred a variety of responses from farmers.
Late 1800's Combine -- pulled by 12-24 horses
A. Improvements in mechanization helped agricultural production increase substantially and contributed to declines in food prices.
B. Many farmers responded to the increasing consolidation in agricultural markets and their dependence on the evolving railroad system by creating local and regional cooperative organizations.
C. Economic instability inspired agrarian activists to create the People's Party (Populists), which called for a stronger governmental role in regulating the American economic system.
William Jennings Bryan's Cross of Gold speech, advocating for a US silver standard
Key Concept 6.2 --The migrations that accompanied industrialization transformed both urban and rural areas of the United States and caused dramatic social and cultural change.
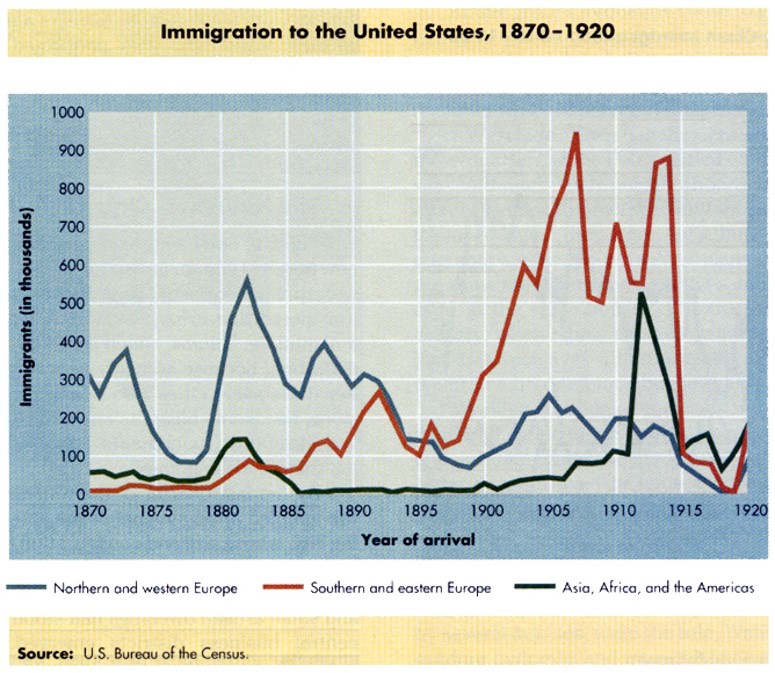
I. International and internal migration increased urban populations and fostered the growth of a new urban culture.
A. As cities became areas of economic growth featuring new factories and businesses, they attracted immigrants from Asia and from southern and eastern Europe, as well as African American migrants within and out of the South. Many migrants moved to escape poverty, religious persecution, and limited opportunities for social mobility in their home countries or regions.
B. Urban neighborhoods based on particular ethnicities, races, and classes provided new cultural opportunities for city dwellers.
C. Increasing public debates over assimilation and Americanization accompanied the growth of international migration. Many migrants negotiated compromises between the cultures they brought and the cultures they found in the United States.
D. In an urban atmosphere where the access to power was unequally distributed, political machines thrived, in part by providing immigrants and the poor with social services.
Tammany Hall, New York City 1867
E. Corporations need for managers and for male and female clerical workers as well as increased access to educational institutions, fostered the growth of a distinctive middle class. A growing amount of leisure time also helped to expand consumer culture.
II. Larger numbers of migrants moved to the West in search of land and economic opportunity, frequently provoking competition and violent conflict.
A. The building of transcontinental railroads, the discovery of mineral resources, and government policies promoted economic growth and created new communities and centers of commercial activity.
B. In hopes of achieving self sufficiency and independence, migrants moved to both rural and boomtown areas of the West for opportunities, such as building the railroads, mining, farming, and ranching.
C. As migrant populations increased in number and the American bison population was decimated, competition for land and resources in the West among white settlers, American Indians, and Mexican Americans led to an increase in violent conflict.
•In 1868 a Kansas Pacific locomotive had to wait 8 hours for a large herd of buffalo to cross a track => RR policy becomes to destroy buffalo
Huge pile of Buffalo skulls
D. The US Government violated treaties with American Indians and responded to resistance with military force, eventually confining American Indians to reservations and denying tribal sovereignity.
E. Many American Indians preserved their cultures and tribal identities despite government policies promoting assimilation, and they attempted to develop self-sustaining economic practices.
Ghost Dance at Wounded Knee
Carlisle Indian School, 1898
Key Concept 6.3 -- The Gilded Age produced new cultural and intellectual movements, public reform efforts, and political debates over economic and social policies.
I. New cultural and intellectual movements both buttressed and challenged the social order of the Gilded Age.
A. Social commentators advocated theories later described as Social Darwinism to justify the success of those at the top of the socioeconomic structure as both appropriate and inevitable.
B. Some business leaders argued that the wealthy had a moral obligation to help the less fortunate and improve society, as articulated in the idea known as the Gospel of Wealth, and they made philanthropic contributions that enhanced educational opportunities and urban environments.
C. A number of artists and critics, including agrarians, utopians, socialists, and advocates of the Social Gospel, championed alternative visions for the economy and US society.
II. Dramatic social changes in the period inspired political debates over citizenship, corruption, and the proper relationship between business and government.
A. The major political parties appealed to lingering divisions from the Civil War and contended over tariffs and currency issues, even as reformers argued that economic greed and self-interest had corrupted all levels of government.
B. Many women sought greater equality with men, often joining voluntary organizations, going to college, promoting social and political reform, and, like Jane Addams, working in settlement houses to help immigrants adapt to US language and customs.
•Hull House was one the first prominent settlement houses in American cities => it once covered a city block on Chicago’s South side and provided services for the city’s poor
C. The Supreme Court decision in Plessy v Ferguson that upheld racial segregation helped to mark the end of most of the political gains African Americans made during Reconstruction. Facing increased violence, discrimination, and scientific theories of race, African Americans continued to fight for political and social equality.
WEB DuBois, Founder of the NAACP
Booker T Washington, Founder of Tuskegee Institute
Unit VI in Maps
Pacific Railway Act
Southern Economic Activity in the Late 1800's
Native Reservations in the Western US (late 1800's)
Southern Sharecropping in the Late 1800's
Videos and Links
The Following sites and materials are useful in reviewing the content of this unit
AP Notes -- American Pageant Textbook Summaries
Click HERE to link to the textbook summary page
Gilder Lehrman AP US History
The Gilder Lehrman site offers review videos, key concepts and an interactive timeline of the era. It also contains study guides and sample essays from key topics in the time period. Visit the Gilder Lehrman AP US History Unit VI website HERE